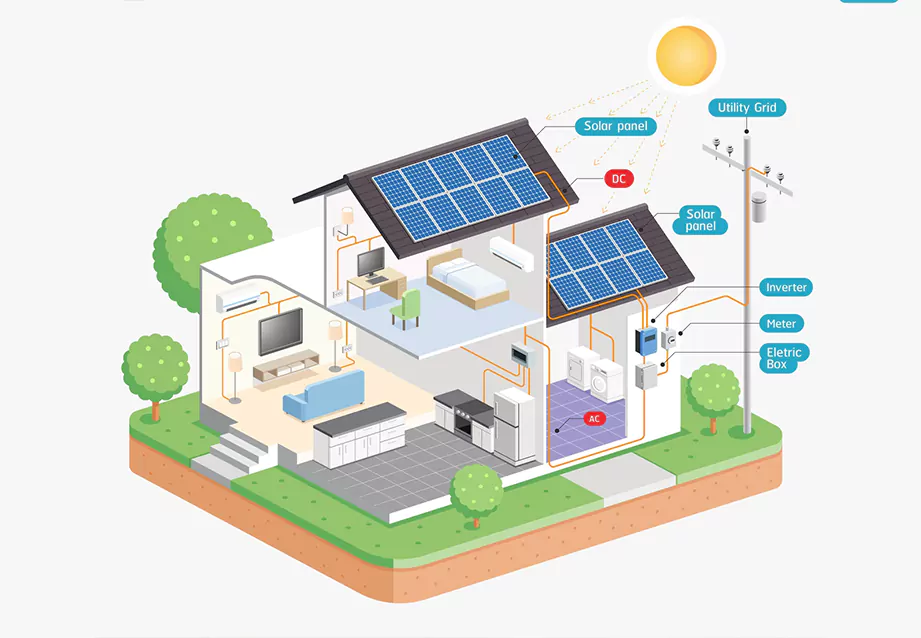
There are many benefits of installing a Battery Energy Storage System. These systems are available for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. To learn more about battery energy storage systems, read the following article. It will cover Lithium-ion batteries, Inverters, Costs, and Applications. Here are some of the advantages:
Applications of battery energy storage systems
There are many applications for battery energy storage systems, but none are cost-effective by itself. In fact, only a single system may be cost-effective, while using several can provide substantial benefits to a business. However, the benefits and costs of combining multiple systems are not clearly expressed. In some cases, the combination of different systems is economically beneficial, and the cost of one system may exceed the benefits of the others. It is essential to ensure that different systems offer similar operational and technical characteristics.
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) can help balance load on the electrical grid between off-peak and on-peak hours. Electricity demand varies throughout the day, based on the time of year, and other factors. Higher electricity demand during peak hours means a higher price, while lower electricity prices are common during off-peak hours. With battery energy storage systems, peak shaving can be easily achieved. The system can also contribute to grid stability by ensuring reliability, which is an important feature of any electrical system.
Other applications of battery energy storage systems include the creation of microgrids and grid services for businesses. These microgrids can be scaled up and down as needed, making them cost-effective and attractive to growing businesses and communities. Traditional electric bills typically have demand fees that account for 30-70% of the total cost. Batteries can store energy during times of lower demand, reducing costs without compromising energy access. This makes battery energy storage systems a particularly viable option for customers without net metering.
Lithium-ion batteries
The basic function of a lithium-ion battery is to store energy. Lithium ions are the primary component of this type of battery, and their electrochemical behavior is determined by the cathode. The cathode generally consists of a complex lithiated compound material, which may be composed of several types of lithium metal oxides. Different cathode types will have different results in terms of battery performance. Generally, lithium-ion batteries have low ionic and diffusion coefficients. This causes them to have a low energy density, which ultimately results in a lower EE and lifetime.
Costs
The costs of a battery energy storage system vary significantly from one project to the next. Lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used for energy storage systems, are cheapest when deployed in large projects that use a large amount of electricity. But most projects are not large enough to require such a high volume of electricity. The lowest lithium-ion battery pricing is $137 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). Instead, costs will be closer to US$150 to $170 per kWh.
Lithium-ion battery prices have decreased sharply in recent years, spurring massive investment in the technology and mass manufacturing. But lithium prices have gone up nearly 900% since 2021, despite their dramatic fall in price. Meanwhile, energy and freight costs have gone up significantly as a result of the Covid pandemic, as well as the war in Ukraine. Lithium prices are now more than double what they were in 2010.
While battery electricity storage systems have a large potential for cost reduction and deployment, there are certain costs that may limit their adoption. As battery manufacturing facilities improve, cost-effective batteries will be developed. This could mean a 50 to 60 percent decrease in installed costs for battery electricity systems by 2030. The cost of battery cells could even come down further, and overall capital cost of battery energy storage systems could drop to USD 200 per kilowatt-hour by 2030.
Manufacturing process
In order to achieve a high-quality final product, battery manufacturing processes must be digitalized and integrated into an Industry 4.0 system. Digital twins of production processes will allow engineers to predict the performance and structure of the final product, and they will also improve monitoring and optimization capabilities. They can also be networked with each other to improve the overall efficiency of the production process. But before implementing these technologies in manufacturing, it is important to understand their purpose and locations.
The manufacturing process for a battery energy storage system is closely linked to recycling. A battery’s life cycle begins with the manufacturing of its cells and ends with its disposal. Batteries are typically recycled through a process known as “cycling” or “remanufacturing.” This process is highly specialized and complex, and it is vital that manufacturers understand how to do it safely. In addition, the circular economy aims to promote battery recycling by reducing the amount of waste that is created.
The manufacturing process for a battery cell consists of a series of steps, each of which has a varying impact on the performance and quality of the final product. These steps influence the operation of machines, process chains, and other production system elements. Developing process models is the first step to bringing these simulations to fruition. These models describe the characteristics of the processing units and how they interact with the rest of the production system.
For more effective data analytics, manufacturing process data from production lines should be collected from different sources. Process parameters, peripheral devices, and product characteristics should be collected and analysed using powerful algorithms and computing systems. The data from these measurements should also be able to be distributed to various employees, making it easier for them to intervene during unplanned downtime and make conscious decisions for improvement. There are some key steps in the manufacturing process that should be automated to ensure a better end-product.